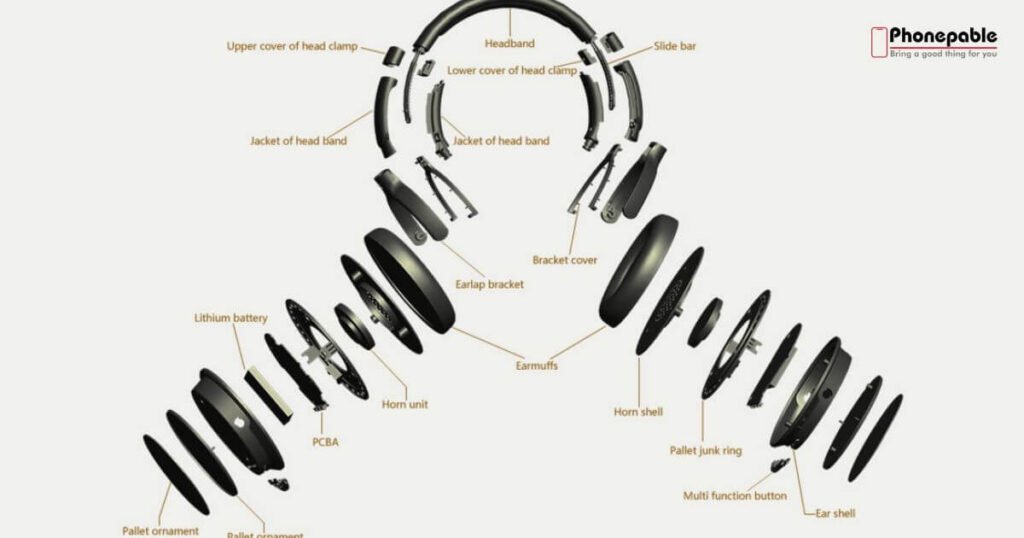
Headphones aren’t just about looks or brand—they’re complex audio devices made of many tiny yet crucial components. From the headphone jack to the speaker drivers, every part plays a key role in delivering the sound you love. Discover more headphones on Best headphones studio
Whether you’re a casual listener or an audiophile, understanding the parts of headphones helps you make smarter buying choices, troubleshoot common issues, and even extend the life of your favorite pair. This guide breaks down each piece, showing how these parts work together to create an immersive headphone audio experience in 2025.
What Are the Main Parts of a Headphone?
Headphones are made up of several small but important parts. Each of these parts plays a key role in how sound is delivered to your ears. From driver housings to headphone cushions, every detail matters in the final audio experience.
The parts of over-ear headphones usually include the headband, ear cups, cushions, cables, connectors, and drivers. Understanding these elements will help you choose better headphones and fix small issues like jack-to-cable connection issues or speaker distortion detection.
The Headband – More Than Just a Frame

The headband is the part that goes over your head and connects both ear cups. It’s not just a holder; it also contains headband wiring if your headphones don’t have two cables. The structural design of the headband affects comfort and long-term durability.
Some durable headphone materials like stainless steel and carbon fiber are used for the headband. These make the mechanical integrity of the headband stronger and last longer even with daily use. Adjustable headbands improve the fit and help avoid headphone wear and tear.
Ear Cups and Ear Pads – Where Comfort Meets Acoustics
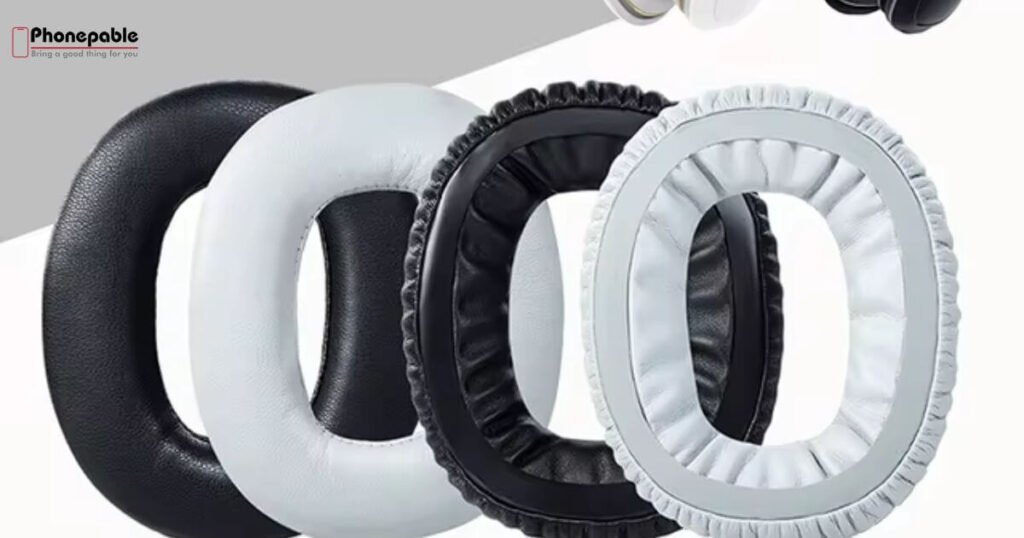

Ear cups cover the ears and hold the speaker drivers. Ear pads, also known as cushions, sit on the ear cups to give comfort and reduce outside noise. High-quality foam ear pads and memory foam cushions improve the comfort and fit of ear pads.
They also boost noise isolation effectiveness, keeping outside sound out. Worn-out pads show cushion degradation signs like cracks, flattening, or discomfort. In that case, headphone cushions replacement is recommended for better sound and comfort.
Drivers – The Heart of Headphone Sound
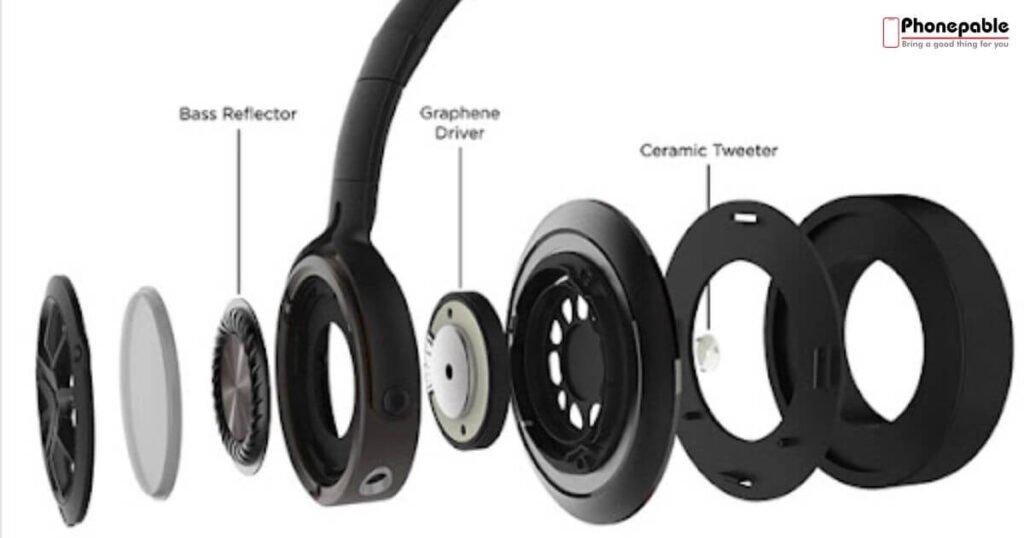

The drivers are the most important part. They change electrical signals into sound. Most headphones have dynamic drivers, but some high-end ones use planar magnetic or balanced armature types.
Larger drivers, like 40mm or 50mm, give better bass and clear audio reproduction. They sit inside the headphone driver housing and are key to overall speaker quality in headphones. Damaged drivers can cause buzzing due to worn-out speakers.
Cables and Connectors – Wired vs Wireless Explained
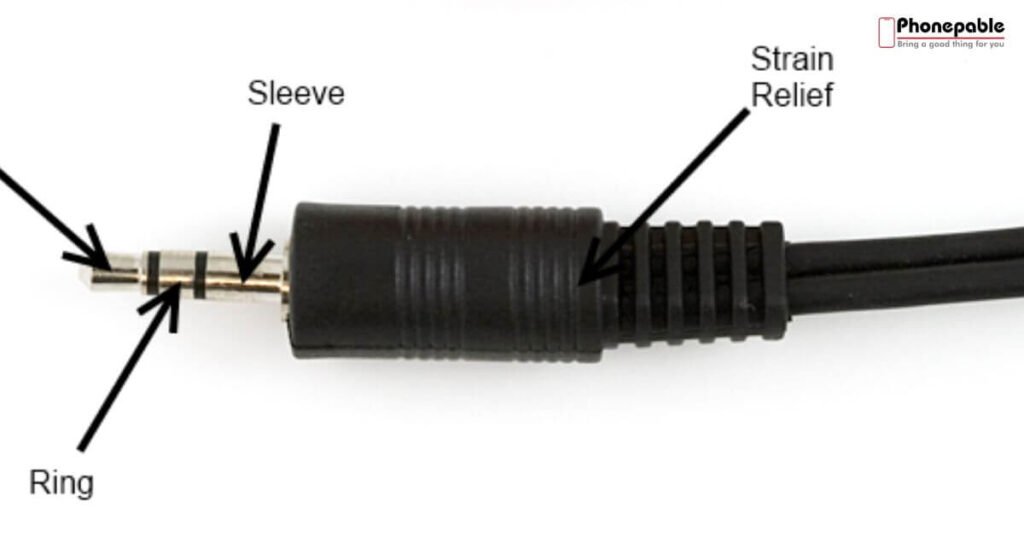

Wired headphone structure includes cables and connectors, which send signals from your device to the drivers. A common issue is cable fraying symptoms that cause sound to drop or only work in one ear. This is usually due to bending or pulling.
The jack-to-cable connection issues are also common, and may require headphone jack repair. Wireless headphones use Bluetooth, which removes these physical problems but adds pairing and battery concerns.
Common Cable & Jack Issues
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
| One side no sound | Frayed wire near jack | Replace cable |
| Sound cuts in/out | Loose jack connection | Secure or replace jack |
| No sound at all | Broken cable core | Full cable replacement |
Speaker Diaphragm – How Your Music Comes Alive
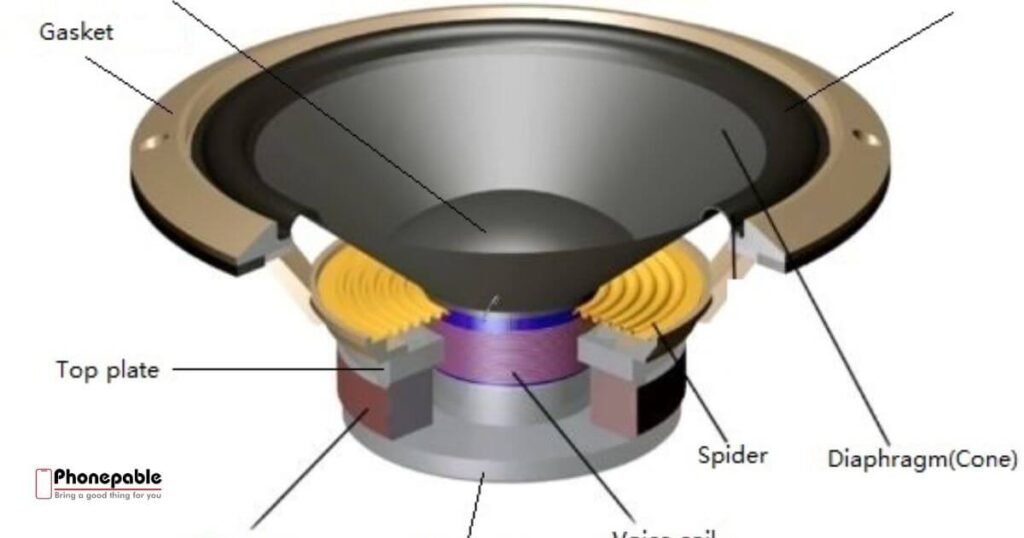
The diaphragm is a thin sheet inside the driver that vibrates to make sound. It reacts to electrical signals and produces sound waves. The audio signal transmission needs to be smooth for the diaphragm to work well.
High-quality diaphragms deliver better frequency response and clarity. Materials like Mylar or titanium help avoid electrical signal disruption, giving users a clean and dynamic sound.
Housing or Enclosure – Shaping the Soundstage
The housing holds the drivers and helps shape how the sound reaches your ears. A good enclosure enhances noise isolation effectiveness and gives more accurate soundstage.
Open-back housings give a wider sound but let in outside noise. Closed-back housings offer better ambient noise rejection. Well-designed headphone driver housing also prevents vibration distortion.
Foam and Padding – Why Your Ears Deserve Softness
Padding adds comfort and supports better noise sealing. Materials like memory foam cushions and protein leather give long-lasting use. Foam material for noise blocking is essential for good noise isolation ear pads.
Signs of worn padding include cracks, loss of shape, or discomfort. This leads to cushion degradation signs, making replacement headphone parts necessary. Replacing these regularly improves both fit and sound.
Microphones and Inline Controls – Smart Features in Modern Headphones
Many headphones today have built-in microphones for calls or voice commands. Inline controls help users change volume, skip tracks, or mute calls without using the phone.
Smart features like voice assistant support and multi-device pairing rely on proper wiring and placement. Bad wiring can lead to broken mic function, which is why repairable headphone elements matter.
Battery and Charging Components in Wireless Headphones
Wireless headphones have batteries and charging ports inside. These should be lightweight yet powerful. The charging speed and battery life affect your daily use experience.
Most use lithium-ion batteries, which offer fast charging but require good headphone care tips. Protecting the charging port and using proper adapters can extend the battery health of your headphones.
ANC Components – What Powers Noise Cancellation?
ANC (Active Noise Cancellation) uses microphones and processors to block out outside noise. It needs power, so it affects battery life in wireless headphones. The system listens to outside sounds and creates an opposite signal.
This signal cancels noise like traffic or airplane hum. Good ANC depends on the audio signal processing chip, microphone quality, and overall headphone audio experience. Poor ANC shows weak ambient sound rejection.
Passive vs Active Noise Isolation
| Feature | Passive Isolation | Active Noise Cancellation |
| Method | Foam padding | Microphones + Anti-sound |
| Power Needed | No | Yes |
| Best For | Mid-level noise | Loud environments |
Final Thoughts – Understanding Parts Means Buying Better Headphones
Knowing the parts of headphones helps you make smart buying decisions. It also helps fix minor problems like jack-to-cable issues or worn ear pads without replacing the whole set. Regular checks and care increase headphone longevity.
Better knowledge of headphone components means better sound, longer life, and more comfort. Keep an eye out for signs of damage. With this guide, you can enjoy better sound and save money by replacing only what’s needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the parts of headphones called?
They include the headband, ear cups, ear cushions, drivers, cables, connectors, and sometimes batteries or mics. - What do you call the circular thing at the end of a headset?
It’s called the headphone jack or 3.5mm audio plug. - What are the rubber pieces on headphones called?
They’re called ear tips or ear cushions depending on the headphone type. - How do you get ear wax out of headphones?
Use a dry brush or soft cloth, and clean tips separately with alcohol if needed. - What is the structure of headphones?
Headphones have a headband, drivers, cushions, connectors, and a housing for sound delivery. - How to clean ear cushions on headphones?
Wipe them gently with a damp cloth and let them air dry fully.

